This article covers:
Because MongoDB contains unstructured data, Metabase takes a different approach to syncing your database’s metadata. To get a sense of the schema, Metabase will scan the first 200 documents of each collection in your MongoDB. This sampling helps Metabase do things like differentiate datetime fields from string fields, and provide people with pre-populated filters. The reason Metabase only scans a sample of the documents is because scanning every document in every collection on every sync would be put too much strain on your database. And while the sampling does a pretty good job keeping Metabase up to date, it can also mean that new fields can sometimes fall through the cracks, leading to visualization issues, or even fields failing to appear in your results. For more info, check out our troubleshooting guide.
Go to Admin -> Databases, and click the Add database button. Select MongoDB from the dropdown.
There are two ways to connect to MongoDB:
The default way to connect to MongoDB is to fill out your connection details in the fields Metabase provides:
Additional settings:
Use DNS SRV when connecting Using this option requires that provided host is a FQDN. If connecting to an Atlas cluster, you might need to enable this option. If you don’t know what this means, leave this disabled.
Use a secure connection (SSL)? Enable SSL and paste the contents of the server’s SSL certificate chain in the input text box. This option is available for this method of connection only (i.e. you cannot include a certificate when connecting with a connection string).
If you’d prefer to connect to MongoDB using a connection string, click on Paste a connection string. The Metabase user interface will update with a field to paste your connection string.
Metabase currently does NOT support the following connection string parameters:
tlsCertificateKeyFiletlsCertificateKeyFilePasswordtlsCAFileIf you need to use a certificate, connect via the default method and enable Use a secure connection(SSL).
You can enter a self-signed certificate via the Metabase UI (though not when using a connection string), or you can use the command line to add a self-signed certificate.
cp /usr/lib/jvm/default-jvm/jre/lib/security/cacerts ./cacerts.jks
keytool -import -alias cacert -storepass changeit -keystore cacerts.jks -file my-cert.pem
Then, start Metabase using the store:
java -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=cacerts.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit -jar metabase.jar
Learn more about configuring SSL with MongoDB.
To make sure you are using the correct connection configuration:
Log into your Atlas cluster
Select the cluster you want to connect to, and click Connect.

Click Connect Your Application.

Select Java and 3.6 or later.
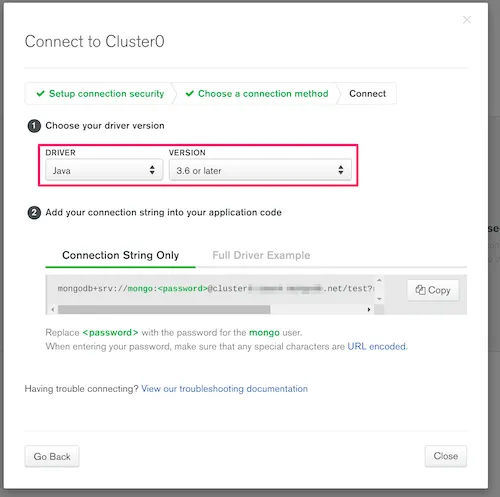
The resulting connection string has the relevant information to provide to Metabase’s Add a Database form for MongoDB.
You will likely want to select the option Use DNS SRV, which newer Atlas clusters use by default.
DNS SRV, which is the recommended method for newer Atlas clusters.0.0.0.0/0? Whitelisting this address allows connections from any IP addresses. If you know the IP address(es) or CIDR block of clients, use that instead.?readPreference=secondary argument in the connection string, which allows Metabase to read from a secondary server instead of consuming resources from the primary server.